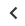Thematic
Fire resistance limits of ducts and installation standards
The fire resistance limit of ducts directly affects the fire protection capability of the entire fire suppression system of a construction project in general and the smoke extraction and ventilation system in particular. In unfortunate cases of a fire outbreak, a strong fire resistance capacity ensures safety for human lives.
Due to these reasons, the government has established regulations concerning the fire resistance limits of ducts for specific installation positions to enhance construction quality and safeguard the public. So, what are these government-mandated limits and how are the installation standards defined?
The fire resistance limits of ducts as specified by government regulations

Fire-resistant ducts and government regulations
The fire resistance limit of ducts refers to the duration from when the duct is exposed to fire until there is a loss of physical integrity, thermal insulation capability, or structural collapse. For ducts, the fire resistance limit is determined by the EI standard in fire resistance, which includes:
- Integrity: The time during which the duct is exposed to fire until a loss of integrity occurs, such as deformation, melting, or collapse.
- Insulation: The time during which the duct is exposed to fire until a loss of material insulation stability occurs.
According to QCVN 06:2021/BXD, the ventilation system of a construction project must meet the minimum fire resistance time at installation positions. Consequently, ducts with EI standard must obtain certification from authorized agencies through fire testing.
Installation standards for fire-resistant duct systems according to QCVN 06:2021/BXD
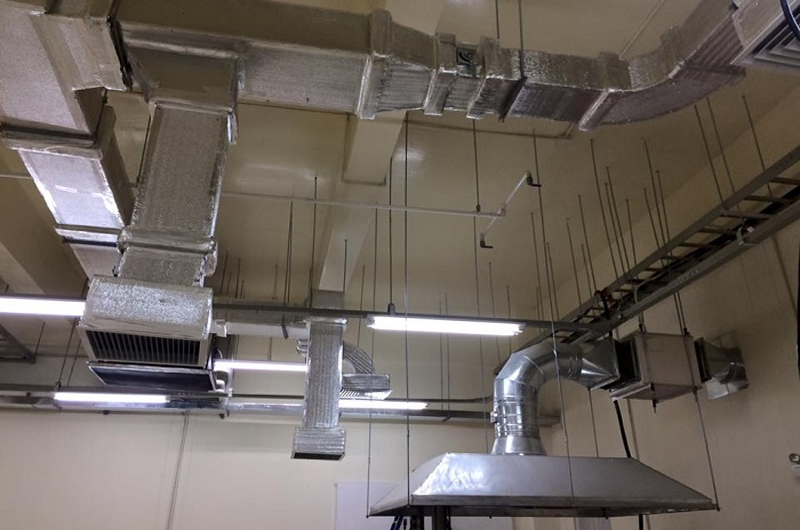
Some installation standards for fire-resistant ducts according to QCVN 06:2021/BXD
As outlined in QCVN 06/2021/BXD, the requirements for the EI standard in fire-resistant materials vary depending on the installation position of the ducts. Some of the most commonly used standards today include: EI 30, EI 45, EI 60, EI 90, EI 120, and EI 180 fire-resistant ducts. The installation positions are regulated as follows:
- Ducts and smoke channels outside the fire compartment, in cases where they pass through walls or fire compartment floors and no normally open valves are installed, must meet the EI 120-minute standard.
- Ducts and smoke channels inside the fire compartment, for smoke extraction from enclosed parking levels, must meet the EI 60-minute standard.
- Vertical ducts inside the fire compartment that serve the purpose of smoke extraction in that area must meet the EI 45-minute standard.
- Remaining ducts in the system must meet at least the EI 30-minute standard.
Consequently, the minimum fire resistance limit of ducts in all circumstances must be EI 30 or higher, increasing according to specific positions. Additionally, for ducts located within technical shafts that have been enveloped by other fire-resistant components meeting the standard, a specific fire resistance limit is not required.
Furthermore, an integral component alongside ducts in ventilation systems is the fire damper. In the mentioned regulations, a normally open fire damper is one that is placed in an open state and automatically closes in the event of a fire or explosion incident. Fire dampers in ventilation systems also need to meet EI standards for fire resistance at the positions they serve.
To ensure optimal usability, the fire-resistant duct solution should employ high-quality fire-resistant materials. Among these, the KHS.HF.M thermal insulation panel is known as a preferred choice due to its exceptional fire resistance and insulation properties, finding widespread application in duct solutions like:
- Smoke spill system: This system only operates in the event of a fire or chemical spill.
- Air conditioning ventilation system: This system operates to remove stale air and provide fresh oxygen to the interior space.
- Stairwell ventilation system: This system creates positive pressure in stairwell and emergency exit areas.
The fire resistance limit of ducts in ventilation systems is a crucial factor determining the fire protection capability of the entire fire suppression system
Update the latest topic
Update highlights
Consultation on fire and explosion prevention solutions